Word2vec for Embedding
Word embedding is one of the most popular representation of document vocabulary. . Rather than build a sparse representation with One hot encoding we can build dense vector for each word
“You shall know a word by the company it keeps”(J. R. Firth 1957: 11) is one of the most successful ideas of modern statistical NLP.

Banking Vector = $\left[ \begin{array} { c } { 0.286 } \ { 0.792 } \ { - 0.177 } \ { - 0.107 } \ { 0.109 } \ { - 0.542 } \ { 0.349 } \ { 0.271 } \end{array} \right)$
Word2vec (Mikolovet al. 2013) is a framework for learning word vectors
- We have a large corpus of text
- Every word in a fixed vocabulary is represented by a vector
- Go through each position tin the text, which has a center word c and context (“outside”) words o
- Use the similarity of the word vectors for c and o to calculate the probability of o given c (or vice versa)
- Keep adjusting the word vectors to maximize this probability
For a center word c and a context word o:
We can then optimize using gradient descent.
It has 2 model variants:
1.Skip-grams (SG)Predict context (”outside”) words (position independent) given center word
2.Continuous Bag of Words (CBOW)Predict center word from (bag of) context words
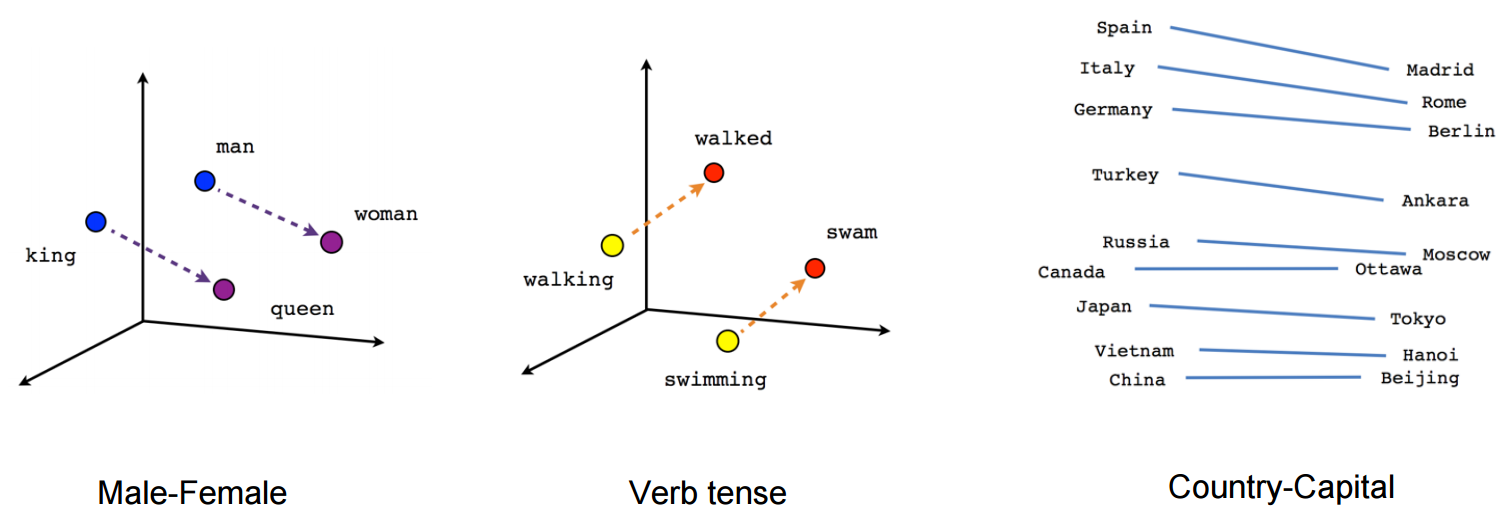
It is capable of capturing context of a word in a document, semantic and syntactic similarity, relation with other words
Word2vec

from __future__ import print_function, division
from builtins import range
import json
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scipy.special import expit as sigmoid
from sklearn.utils import shuffle
from datetime import datetime
# from util import find_analogies
from scipy.spatial.distance import cosine as cos_dist
from sklearn.metrics.pairwise import pairwise_distances
from glob import glob
import os
import sys
import string
sys.path.append(os.path.abspath('..'))
from rnn_class.brown import get_sentences_with_word2idx_limit_vocab as get_brown
# unfortunately these work different ways
def remove_punctuation_2(s):
return s.translate(None, string.punctuation)
def remove_punctuation_3(s):
return s.translate(str.maketrans('','',string.punctuation))
if sys.version.startswith('2'):
remove_punctuation = remove_punctuation_2
else:
remove_punctuation = remove_punctuation_3
def get_wiki():
V = 20000
files = glob('../large_files/enwiki*.txt')
all_word_counts = {}
for f in files:
for line in open(f):
if line and line[0] not in '[*-|=\{\}':
s = remove_punctuation(line).lower().split()
if len(s) > 1:
for word in s:
if word not in all_word_counts:
all_word_counts[word] = 0
all_word_counts[word] += 1
print("finished counting")
V = min(V, len(all_word_counts))
all_word_counts = sorted(all_word_counts.items(), key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)
top_words = [w for w, count in all_word_counts[:V-1]] + ['<UNK>']
word2idx = {w:i for i, w in enumerate(top_words)}
unk = word2idx['<UNK>']
sents = []
for f in files:
for line in open(f):
if line and line[0] not in '[*-|=\{\}':
s = remove_punctuation(line).lower().split()
if len(s) > 1:
# if a word is not nearby another word, there won't be any context!
# and hence nothing to train!
sent = [word2idx[w] if w in word2idx else unk for w in s]
sents.append(sent)
return sents, word2idx
def train_model(savedir):
# get the data
sentences, word2idx = get_wiki() #get_brown()
# number of unique words
vocab_size = len(word2idx)
# config
window_size = 5
learning_rate = 0.025
final_learning_rate = 0.0001
num_negatives = 5 # number of negative samples to draw per input word
epochs = 20
D = 50 # word embedding size
# learning rate decay
learning_rate_delta = (learning_rate - final_learning_rate) / epochs
# params
W = np.random.randn(vocab_size, D) # input-to-hidden
V = np.random.randn(D, vocab_size) # hidden-to-output
# distribution for drawing negative samples
p_neg = get_negative_sampling_distribution(sentences, vocab_size)
# save the costs to plot them per iteration
costs = []
# number of total words in corpus
total_words = sum(len(sentence) for sentence in sentences)
print("total number of words in corpus:", total_words)
# for subsampling each sentence
threshold = 1e-5
p_drop = 1 - np.sqrt(threshold / p_neg)
# train the model
for epoch in range(epochs):
# randomly order sentences so we don't always see
# sentences in the same order
np.random.shuffle(sentences)
# accumulate the cost
cost = 0
counter = 0
t0 = datetime.now()
for sentence in sentences:
# keep only certain words based on p_neg
sentence = [w for w in sentence \
if np.random.random() < (1 - p_drop[w])
]
if len(sentence) < 2:
continue
# randomly order words so we don't always see
# samples in the same order
randomly_ordered_positions = np.random.choice(
len(sentence),
size=len(sentence),#np.random.randint(1, len(sentence) + 1),
replace=False,
)
for pos in randomly_ordered_positions:
# the middle word
word = sentence[pos]
# get the positive context words/negative samples
context_words = get_context(pos, sentence, window_size)
neg_word = np.random.choice(vocab_size, p=p_neg)
targets = np.array(context_words)
# do one iteration of stochastic gradient descent
c = sgd(word, targets, 1, learning_rate, W, V)
cost += c
c = sgd(neg_word, targets, 0, learning_rate, W, V)
cost += c
counter += 1
if counter % 100 == 0:
sys.stdout.write("processed %s / %s\r" % (counter, len(sentences)))
sys.stdout.flush()
# break
# print stuff so we don't stare at a blank screen
dt = datetime.now() - t0
print("epoch complete:", epoch, "cost:", cost, "dt:", dt)
# save the cost
costs.append(cost)
# update the learning rate
learning_rate -= learning_rate_delta
# plot the cost per iteration
plt.plot(costs)
plt.show()
# save the model
if not os.path.exists(savedir):
os.mkdir(savedir)
with open('%s/word2idx.json' % savedir, 'w') as f:
json.dump(word2idx, f)
np.savez('%s/weights.npz' % savedir, W, V)
# return the model
return word2idx, W, V
def get_negative_sampling_distribution(sentences, vocab_size):
# Pn(w) = prob of word occuring
# we would like to sample the negative samples
# such that words that occur more often
# should be sampled more often
word_freq = np.zeros(vocab_size)
word_count = sum(len(sentence) for sentence in sentences)
for sentence in sentences:
for word in sentence:
word_freq[word] += 1
# smooth it
p_neg = word_freq**0.75
# normalize it
p_neg = p_neg / p_neg.sum()
assert(np.all(p_neg > 0))
return p_neg
def get_context(pos, sentence, window_size):
# input:
# a sentence of the form: x x x x c c c pos c c c x x x x
# output:
# the context word indices: c c c c c c
start = max(0, pos - window_size)
end_ = min(len(sentence), pos + window_size)
context = []
for ctx_pos, ctx_word_idx in enumerate(sentence[start:end_], start=start):
if ctx_pos != pos:
# don't include the input word itself as a target
context.append(ctx_word_idx)
return context
def sgd(input_, targets, label, learning_rate, W, V):
# W[input_] shape: D
# V[:,targets] shape: D x N
# activation shape: N
# print("input_:", input_, "targets:", targets)
activation = W[input_].dot(V[:,targets])
prob = sigmoid(activation)
# gradients
gV = np.outer(W[input_], prob - label) # D x N
gW = np.sum((prob - label)*V[:,targets], axis=1) # D
V[:,targets] -= learning_rate*gV # D x N
W[input_] -= learning_rate*gW # D
# return cost (binary cross entropy)
cost = label * np.log(prob + 1e-10) + (1 - label) * np.log(1 - prob + 1e-10)
return cost.sum()
def load_model(savedir):
with open('%s/word2idx.json' % savedir) as f:
word2idx = json.load(f)
npz = np.load('%s/weights.npz' % savedir)
W = npz['arr_0']
V = npz['arr_1']
return word2idx, W, V
def analogy(pos1, neg1, pos2, neg2, word2idx, idx2word, W):
V, D = W.shape
# don't actually use pos2 in calculation, just print what's expected
print("testing: %s - %s = %s - %s" % (pos1, neg1, pos2, neg2))
for w in (pos1, neg1, pos2, neg2):
if w not in word2idx:
print("Sorry, %s not in word2idx" % w)
return
p1 = W[word2idx[pos1]]
n1 = W[word2idx[neg1]]
p2 = W[word2idx[pos2]]
n2 = W[word2idx[neg2]]
vec = p1 - n1 + n2
distances = pairwise_distances(vec.reshape(1, D), W, metric='cosine').reshape(V)
idx = distances.argsort()[:10]
# pick one that's not p1, n1, or n2
best_idx = -1
keep_out = [word2idx[w] for w in (pos1, neg1, neg2)]
# print("keep_out:", keep_out)
for i in idx:
if i not in keep_out:
best_idx = i
break
# print("best_idx:", best_idx)
print("got: %s - %s = %s - %s" % (pos1, neg1, idx2word[best_idx], neg2))
print("closest 10:")
for i in idx:
print(idx2word[i], distances[i])
print("dist to %s:" % pos2, cos_dist(p2, vec))
def test_model(word2idx, W, V):
# there are multiple ways to get the "final" word embedding
# We = (W + V.T) / 2
# We = W
idx2word = {i:w for w, i in word2idx.items()}
for We in (W, (W + V.T) / 2):
print("**********")
analogy('king', 'man', 'queen', 'woman', word2idx, idx2word, We)
analogy('king', 'prince', 'queen', 'princess', word2idx, idx2word, We)
analogy('miami', 'florida', 'dallas', 'texas', word2idx, idx2word, We)
analogy('einstein', 'scientist', 'picasso', 'painter', word2idx, idx2word, We)
analogy('japan', 'sushi', 'germany', 'bratwurst', word2idx, idx2word, We)
analogy('man', 'woman', 'he', 'she', word2idx, idx2word, We)
analogy('man', 'woman', 'uncle', 'aunt', word2idx, idx2word, We)
analogy('man', 'woman', 'brother', 'sister', word2idx, idx2word, We)
analogy('man', 'woman', 'husband', 'wife', word2idx, idx2word, We)
analogy('man', 'woman', 'actor', 'actress', word2idx, idx2word, We)
analogy('man', 'woman', 'father', 'mother', word2idx, idx2word, We)
analogy('heir', 'heiress', 'prince', 'princess', word2idx, idx2word, We)
analogy('nephew', 'niece', 'uncle', 'aunt', word2idx, idx2word, We)
analogy('france', 'paris', 'japan', 'tokyo', word2idx, idx2word, We)
analogy('france', 'paris', 'china', 'beijing', word2idx, idx2word, We)
analogy('february', 'january', 'december', 'november', word2idx, idx2word, We)
analogy('france', 'paris', 'germany', 'berlin', word2idx, idx2word, We)
analogy('week', 'day', 'year', 'month', word2idx, idx2word, We)
analogy('week', 'day', 'hour', 'minute', word2idx, idx2word, We)
analogy('france', 'paris', 'italy', 'rome', word2idx, idx2word, We)
analogy('paris', 'france', 'rome', 'italy', word2idx, idx2word, We)
analogy('france', 'french', 'england', 'english', word2idx, idx2word, We)
analogy('japan', 'japanese', 'china', 'chinese', word2idx, idx2word, We)
analogy('china', 'chinese', 'america', 'american', word2idx, idx2word, We)
analogy('japan', 'japanese', 'italy', 'italian', word2idx, idx2word, We)
analogy('japan', 'japanese', 'australia', 'australian', word2idx, idx2word, We)
analogy('walk', 'walking', 'swim', 'swimming', word2idx, idx2word, We)
if __name__ == '__main__':
word2idx, W, V = train_model('w2v_model')
# word2idx, W, V = load_model('w2v_model')
test_model(word2idx, W, V)
References:
- Tomas Mikolov, Kai Chen, Greg Corrado, and Jef-frey Dean. 2013a. Efficient Estimation of WordRepresentations in Vector Space. InICLR Work-shop Papers.
- Tomas Mikolov, Ilya Sutskever, Kai Chen, GregCorrado, and Jeffrey Dean. 2013b. Distributedrepresentations of words and phrases and theircompositionality. InNIPS, pages 3111–3119.
- Tomas Mikolov, Wen tau Yih, and GeoffreyZweig. 2013c. Linguistic regularities in con-tinuous space word representations. InHLT-NAACL